TIP:
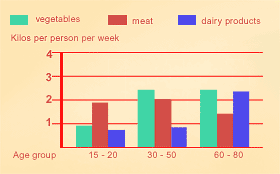
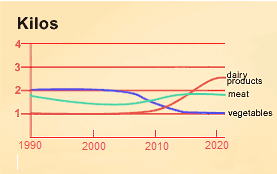
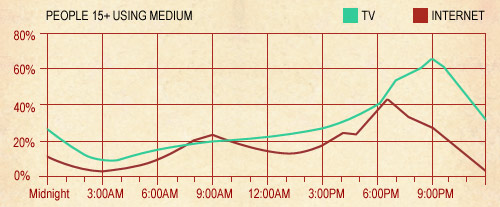
When you are interpreting and then describing visual information you will need to refer to the format that it is presented in. For example, whether it is a graph, a table, a chart, etc.
Remember: You must give a clear overview of the information that is provided, rephrasing the description that is given. If the overview is missing, your mark will be limited to a band score of 5.